PERT Chart Terminology
- Milestone
- Task
- Critical Path
- Critical Activity
- Optimistic Time
- Pessimistic Time
- Most Likely Time
- Expected Time
- Standard deviation of time
- Slack
Milestone
A milestone (known also as a PERT event) is an element of a PERT chart, marking the start or completion of a task or several tasks. It consumes no time and uses no resources. When it marks the completion of one or more activities, it is not "reached" (does not occur) until all of the activities leading to that event have been completed. When task or tasks take the beginning from the milestone, it is called Start milestone (or a predecessor event). Those ones which tasks end in are called Finish milestones (or successor events). Only the Start milestone can become a predecessor event for several tasks, and only the Finish milestone can become a successor event for several tasks.
See how to configure the milestones in AnyChart PERT Charts.
Task
The actual performance of a task which consumes time and requires resources (such as labor, materials, space, machinery). It can be understood as representing the time, effort, and resources required to move from one event to another. A PERT activity cannot be performed until the predecessor event has occurred.
A task is an arrow-shaped element of a PERT chart, representing activity that must be performed. There are two types of tasks: predecessors, which precedes a milestone (event), and successors, which follows a milestone (event).
See how to configure the tasks in AnyChart PERT Charts.
Critical Path
A critical path is the longest possible continuous pathway taken from the initial event to the terminal event (some projects can have several critical paths). It determines the total duration of the project, so any delay along the path means a delay for the whole project. The critical path is calculated by the Critical Path Method (CPM) – an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities.
See how to configure the critical path in AnyChart PERT Charts.
Critical Activity
Critical activity is an activity that has slack equal to zero. An activity with zero slack is not necessarily on the critical path since its path may not be the longest.
Find more about activities and their types in the milestones section in AnyChart PERT and about the critical path in the critical path section in AnyChart PERT.
Optimistic Time
Optimistic time is the minimum possible time required to accomplish an activity or a path, assuming everything proceeds better than is normally expected.
See how to set the optimistic time AnyChart PERT Charts.
Pessimistic Time
Pessimistic time is the maximum possible time required to accomplish an activity or a path, assuming everything goes wrong (but excluding major catastrophes).
See how to set the pessimistic time AnyChart PERT Charts.
Most Likely Time
Most likely time is the best estimate of the time required to accomplish an activity or a path, assuming everything proceeds as normal.
See how to set the most likely time AnyChart PERT Charts.
Expected Time
Expected time is the best estimate of the time required to accomplish an activity (te) or a path (TE), accounting for the fact that things don't always proceed as normal (something goes wrong, something goes better than expected). It is being calculated by the following formula:
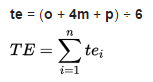 ,
,
where "o" is optimistic activity duration, "p" is pessimistic activity duration and "M" stands for most likely activity duration.
Find more about getting the expected activity duration value in the expected duration section.
Standard deviation of time
The standard deviation of time is the variability of the time for accomplishing an activity (σte) or a path (σTE). It is being calculated by the following formula:
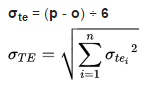 ,
,
where "o" is optimistic activity duration and "p" is pessimistic activity duration.
Find more about getting the value of the standard deviation of time in the Statistics in PERT section.
Slack
Slack (or float) is a measure of the excess time and resources available to complete a task. It is the amount of time that a project task can be delayed without causing a delay in any subsequent tasks (free float) or the whole project (total float). The existence of a slack indicates resources wasting, and zero slack indicates everything goes on schedule.
Find more about managing slacks in the slacks section in AnyChart PERT tutorial.